Refrigeration compressor is a kind of driven fluid machinery, which promotes low-pressure gas to high-pressure gas and is the heart of refrigeration system.
The refrigeration compressor sucks the refrigerant gas of low temperature and low pressure from the suction pipe, then drives the piston to compress the gas through the motor operation, and finally discharges the refrigerant gas with high temperature and high pressure to the exhaust pipe to provide power for the refrigeration cycle, so as to complete a refrigeration cycle: compression → condensation (heat release) → expansion → evaporation (heat absorption)
Compressors can be divided into piston compressor, screw compressor, centrifugal compressor, etc.
Common Types of Refrigeration Compressors: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Piston Compressor

Figure 1: GIF animation of the structure and work of piston compressor
Piston compressor works by changing the working volume composed of cylinder, valve and reciprocating piston in the cylinder.
If we do not consider the volume loss and energy loss in the actual work of the piston compressor (i.e. the ideal working process), then the work of every rotation of the crankshaft of the piston compressor can be divided into suction, compression and exhaust processes.
Working Principle of Piston Compressor
Compression Process
The piston moves upward from the bottom dead center, the suction valve and exhaust valve are closed, and the gas is compressed in the closed cylinder.
As the volume of the cylinder is gradually reduced, the pressure and temperature will gradually increase until the gas pressure in the cylinder is equal to the exhaust pressure.
In a word, compression process is generally regarded as isentropic process.
Exhaust Process
The piston continues to move upward, causing the gas pressure in the cylinder to be higher than the exhaust pressure.
At this moment, the exhaust valve is opened, and the gas in the cylinder is discharged under the condition of equal pressure due to the push of the piston, and then enters the exhaust pipe until the piston moves to the top dead center.
Here, due to the spring force of the exhaust valve and the gravity of the valve plate itself, the exhaust valve closes and the exhaust ends.

Figure 2: GIF animation of the work principle of piston compressor - exhaust process
2. Screw Compressor

Figure 3: GIF animation of work principle of screw compressor
Screw compressor is divided into single screw compressor and double screw compressor.
The single screw compressor was developed by Sinn of France in the 1970s. Because its structure is more reasonable, it has been rapidly applied to the field of national defense, and protected by the countries that developed it. The technology has always been relatively independent.
Twin screw compressor was first proposed by German H. krigar in 1878. It was not until 1934 that A. Lysholm of the Royal Swedish Institute of technology established the SRM technology of screw compressor and began to apply it in industry.
Working Principle of Screw Compressor
Screw compressor cylinder is equipped with a pair of mutually meshing spiral yin and yang rotors. Both rotors have several concave teeth, and they rotate in opposite directions.
The clearance between rotors and between casing and rotor is only 5 ~ 10 threads.
The main rotor (also known as yang rotor or convex rotor) is driven by engine or motor (mostly motor). The other rotor (also known as yin rotor or concave rotor) is driven by the oil film formed by the main rotor through oil injection, or by the synchronous gear at the main rotor end and concave rotor end. So theoretically there is no metal contact in the drive.
The length and diameter of the rotor determine the discharge volume (flow) and discharge pressure of the compressor. The longer the rotor, the higher the pressure. The larger the diameter of the rotor, the greater the flow rate.

Figure 4: GIF animation of working principle of screw compressor
3. Centrifugal Compressor

Figure 5: Structure of centrifugal compressor
Centrifugal compressor, also known as turbine compressor, is mainly used to compress gas. It is mainly composed of rotor and stator.
The rotor consists of impeller and shaft. The impeller has blades, balance disc and a part of shaft seal.
The main body of the stator is the air cylinder, as well as the diffuser, bend, reflux, air bursting pipe, exhaust pipe and other devices.
Working Principle of Centrifugal Compressor
When the impeller rotates at high speed, the gas rotates with the impeller.
Under the action of centrifugal force, the gas is thrown into the diffuser behind, and a vacuum zone is formed at the impeller. At this time, the fresh air from outside enters the impeller.
The impeller rotates continuously, and the gas is continuously inhaled and thrown out, so as to maintain the continuous flow of gas.

Figure 6: GIF animation of the working principle of centrifugal compressor
4. Rotary Compressor

Figure 7: GIF animation of rotor compressor
The rotary compressor is driven by engine or motor (mostly motor).
The other rotor (also known as female rotor or concave rotor) is driven by the oil film formed by the main rotor through oil injection, or by the synchronous gears at the main rotor end and female rotor end.
Working Principle of Rotary Compressor
The spiral rotor groove is filled with gas when passing through the suction port.
When the rotor rotates, the rotor groove is closed by the casing wall to form a compression chamber. At this time, the lubricating oil is injected into the compression chamber to play the role of sealing, cooling and lubrication.
When the rotor rotates and compresses the mixture of lubricant and gas, the volume of the compression chamber decreases and the mixture of oil and gas is compressed to the exhaust port. When the compression chamber passes through the exhaust port, the oil-gas mixture is discharged from the compressor.
These steps complete a process of first inhaling, then compressing, and finally exhausting.
5. Axial Compressor

Figure 8: GIF animation of Axial compressor
Axial compressor is a kind of large air compressor. Its maximum power can reach 150000kw, and its exhaust volume is 20000 m3 / min. its compressor energy efficiency ratio can reach about 90%, which is more energy-saving than centrifuge.
Working Principle of Axial Compressor
Both axial compressor and centrifugal compressor belong to speed compressor, which are called turbine compressor.
The meaning of speed type compressor is that their working principle depends on the blade to do work on the gas, and the flow speed of the gas is greatly improved, and then the kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy.
The meaning of turbine compressor is that they all have high-speed rotating blades.

Figure 9: GIF animation of the working principle of axial compressor
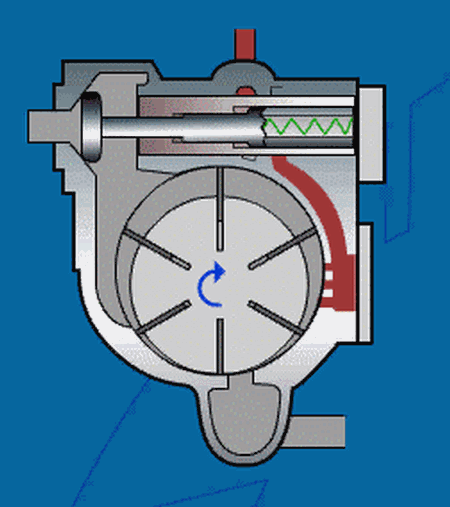
6. Vane Compressor

Figure 10: GIF animation of the work principle of vane compressor
The vane compressor is driven directly at a very low speed.
The rotor is the only continuous running part, on which there are several grooves cut along the length direction, in which there are sliding blades which can slide on the oil film.
The rotor rotates in the stator of the cylinder.
Working Principle of Vane Compressor
The air is drawn in through a filter and a regulating proportional valve. The control valve is mainly used to adjust the air cylinder rotor and the pressure chamber formed by the slide.
The rotor rotation is eccentric relative to the cylinder. The valve plate is installed in the slot of the rotor, and the sliding plate is pushed to the cylinder wall by centrifugal force.
Efficient oil injection system can ensure the minimum loss of compressor cooling and lubricant. A thin oil film formed on the cylinder wall can prevent wear caused by direct contact between metal parts.
Thank you for your reading and more information please visit https://okmarts.com/